Classes: geometric tolerance (shape, direction, position and run)
| Class | Symbol/tag | Description | References (Selection) | ID | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELIAS | K2009 | ||||
| Straightness | | Permissible shape deviation of a line or group of lines from a reference line or reference lines. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 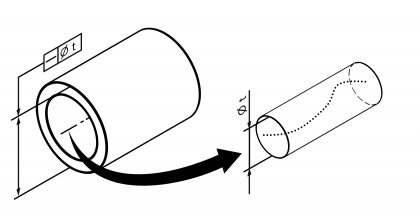 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 12780-1:2014 | 7 | 100 |
| Straightness (shape ⌀) The tolerance range has a circular cross-section, see example. Anmerkung Available from program version 1.4.2.1 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 12780-1:2014 | 121 | 100 | ||
| Flatness | | Permissible shape deviation of a surface from a reference plane. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 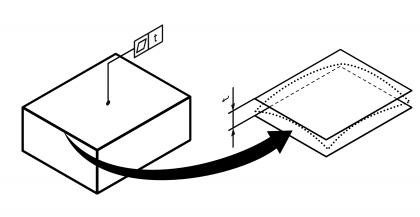 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 12781-1:2011 | 8 | 101 |
| Roundness | | Permissible shape deviation of a circular line or group of circular lines from a reference circle or reference circles. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 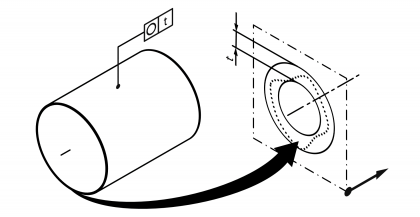 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 12781-1:2011 | 9 | 102 |
| Cylindricity | | Permissible shape deviation of a cylindrical surface from a reference cylinder. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 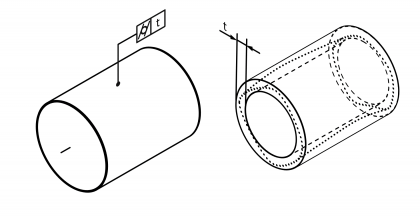 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 12180-1:2011 | 10 | 103 |
| Line profile | | Permissible deviation of a profile line or group of profile lines from a reference line profile or from reference line profiles. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 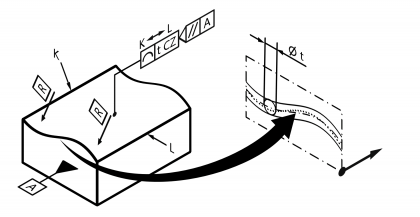 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 1660:2013 | 11 | 104 |
| Surface profile | | Permissible deviation of a profile surface from a reference surface profile. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 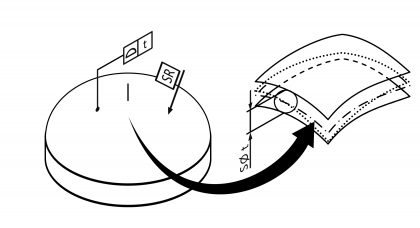 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 1660:2013 | 12 | 105 |
| Parallelism | | Permissible deviation in direction of a line, group of lines or plane from one or several reference lines or plane(s) oriented parallel to it. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 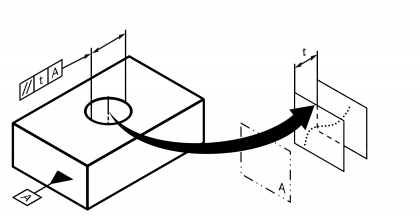 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 | 13 | 108 |
| Parallelism (shape ⌀) The tolerance range has a circular cross-section. Note Available from program version 1.4.2.1 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 12780-1:2014 | 122 | 108 | ||
| Perpendicularity | | Permissible deviation in direction of a line, group of lines or plane from one or several reference lines or plane(s) oriented perpendicular to it. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 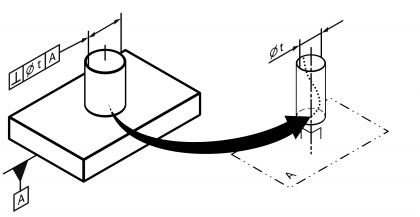 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 | 14 | 107 |
| Perpendicularity (shape ⌀) The tolerance range has a circular cross-section, see example. Note Available from program version 1.4.2.1 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 12780-1:2014 | 123 | 107 | ||
| Inclination | | Permissible deviation in direction of a line, group of lines or plane from one or several reference lines or plane(s) oriented angular (but not perpendicular) to it. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 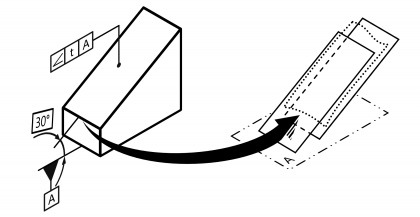 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 | 15 | 106 |
| Inclination (shape ⌀) The tolerance range has a circular cross-section. Note Available from program version 1.4.2.1 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 12780-1:2014 | 124 | 106 | ||
| Position | | Permissible positional deviation of a point, axis or plane from a reference point, reference line or plane positioned to it. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 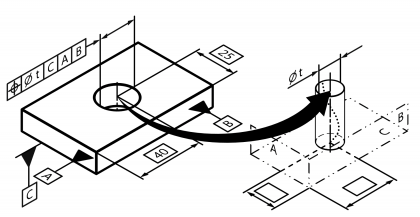 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 5458:1999 | 22 | 109 |
| Position (shape ⌀) The tolerance range has a circular cross-section, see example. Note Available from program version 1.4.2.1 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 12780-1:2014 | 125 | 109 | ||
| Position (shape S⌀) The tolerance range has a circular cross-section. Note Available from program version 1.4.2.1 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 12780-1:2014 | 126 | 109 | ||
| Concentricity | | Permissible positional deviation of a point from a reference point concentric to it. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 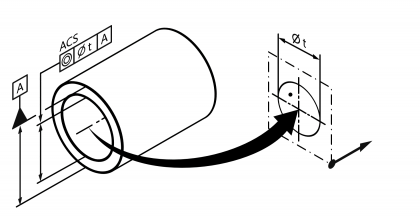 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 | 21 | 110 |
| Concentricity (shape ⌀) The tolerance range has a circular cross-section, see example. Note Available from program version 1.4.2.1 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 12780-1:2014 | 128 | 110 | ||
| Coaxiality | | Permissible positional deviation of straight line from a straight reference line coaxial to it. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example:  | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 | 89 | 663 |
| Coaxiality (shape ⌀) The tolerance range has a circular cross-section, see example. Note Available from program version 1.4.2.1 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 • DIN EN ISO 12780-1:2014 | 127 | 110 | ||
| Symmetry | | Permissible positional deviation of a point, group of points, straight line or plane from one or several reference point(s) or plane(s) lying symmetrical to it. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 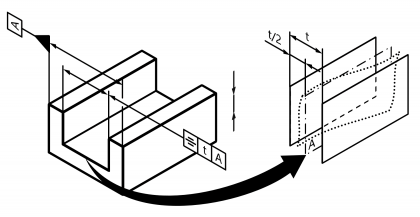 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 | 20 | 111 |
| Radial concentric run-out | | Permissible radial running deviation of a circular line or group of circular lines to one or several reference circle(s) that lies coaxial to it. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 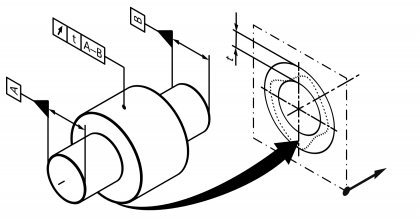 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 | 16 | 112 |
| Axial concentric run-out | | Permissible axial running deviation of a circular line or group of circular lines to one or several reference circle(s) that lies coaxial to it. Also called lateral run. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 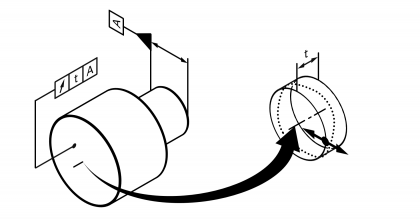 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 | 17 | 118 |
| Radial total concentric run-out | | Permissible radial running deviation of a rotational surface to a rotational surface that lies coaxial to it. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 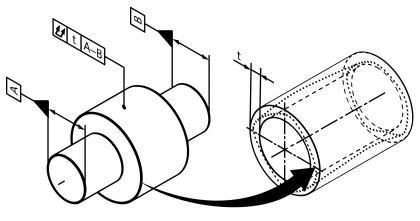 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 | 18 | 113 |
| Axial total concentric run-out | | Permissible axial running deviation of a plane or rotational surface to a plane or rotational surface that lies coaxial to it. Also called total lateral run. Standard measurement unit Millimetres Example: 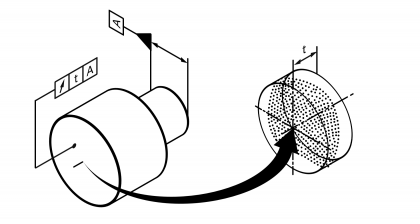 | • DIN EN ISO 1101:2014 | 19 | − |